Confined space attributes to any place, including any vessel, tank, container, pit, bund, chamber, cellar, silos, hulls and storage bins, hoppers, vaults, and sewers or any other similar space which, by virtue of its enclosed nature, creates conditions that give rise to a likelihood of an accident, harm or injury of such a nature as to require emergency action due to the reasonably foreseeable presence of flammable or explosive atmospheres, harmful gas, fume or vapor, free flowing solid or an increasing level of liquid, excess or lack of oxygen, excessively high temperature.
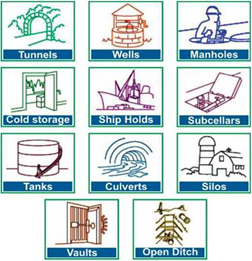
Hazards and Injuries
The hazards associated with the confined spaces are: toxic atmosphere, oxygen deficiency, oxygen enrichment, flammable or explosive atmospheres, flowing liquids or free flowing solids and excessive heat. Other hazards include slippery floors, falls from a height, moving parts of mechanical equipment, corrosive surfaces, noise, electricity, mechanical equipment, dust and radioactive substances. The types of injuries include the injuries arising from fire and explosion, loss of consciousness or asphyxiation arising from harmful gas, fume, vapor, free flowing solids or the lack of oxygen, drowning arising from an increase in the level of a liquid, loss of consciousness arising from an increase in body temperature.
Risk Assessment and Control Strategies
What’s inside the confined space including hazards associated with the inherent nature, structure, contents of condition of the confined space, which are from the present and previous contents, residues, contamination, oxygen deficiency( lower than 19.5%) , oxygen enrichment ( higher than 23.5%) and the structure and layout. What’s created by the work and other activities being carried out such as operation of internal combustion engines exhaust carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, cleaning chemicals which interact with residual substances, flammable substances used, electrocution by electrical equipment, and sparks generating processes such as welding and cutting. What’s outside the confined space in respect of conditions, hazards or substances that could affect a person within the space. The dangers include ingress of substances such as liquids, gases, steam, inert gas, water, raw materials etc, ingress of sources of ignition and inadvertent confinement (closing or blocking of exit routes). For example, inadequate isolation of the confined space from adjacent plant, processes, services and equipment may unexpectedly. Work activities located near the entrance to a confined space, may allow smoke and exhaust fumes, dust or sparks to enter.
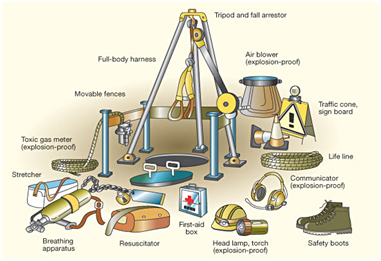
Eliminate the hazards before entering the confined space. Ventilate the space with forced air ventilation in general and on single-point source, exhaust ventilation is the better option available. Good lighting is an essential part of the confined space entry where the emergency backup of lights should also be taken into account. Atmospheric Monitoring against the noxious substances, oxygen concentration and flammable gases, vapors and mists which has to be kept under the Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) should be monitored with the available various digital instruments such as Electrochemical sensors, Infrared sensors, Photo ionization and flame ionization detectors, Colorimetric tubes etc. Communication systems used should be reliable and suitable to the anticipated conditions such as speech, hand signals, telephone, radio, visible lights, alarm system, etc.
Safe system of Work
The main elements to consider when designing a safe system of work are: training, supervision and suitability; permit-to-work procedure; gas purging and ventilation; dangerous residues; testing and monitoring the atmosphere; mechanical, electrical and process isolation; respiratory protective equipment; safe use of work equipment; communications; access and egress; flammable or explosive atmospheres and combustible materials.
Emergency and Rescue Procedures
The emergency arrangements should take account of; training, rescue logistics, rescue equipment and resuscitation procedures and equipment. The basic or advanced, formal or informal and refresher trainings should be provided for the potential rescuers and first aiders involved in the rescue operations. Emergency plans to be developed to have the rescue logistics carried out well such as the means of raising the alarm, handling emergency communication, rescue procedures, use of breathing apparatus, self rescue procedures, examination of ropes, harnesses, lifelines, lifting equipments, first aid equipments, protective clothing and other special equipments.
It is better to join diploma in industrial safety at accredited institute to improve safety awareness in industrial sector. Candidate with Health and safety course certificate would get more preference compared to others.
Shortcuts Leads to Deep cuts!
Safety is a Cheap and Effective Insurance Policy!
Article written by:
Ananth Tamilmaniarasu
HSE Trainer & Consultant,
Green World Group,
Dubai
Our Popular Courses

Nebosh IGC
Nebosh International General Certificate is a job-oriented level-3 certificate in Occupational Health and Safety Management Course

Nebosh IDIP
NEBOSH International Diploma is the highest level certification in HSE management (level-6) helps for students aspiring to become health and safety experts

Safety Diploma
National Safety Diploma Certificate is approved by Government of India, this Certificate holder can apply for job globally

IOSH Courses
Institution of Occupational Safety and Health offering professional qualifications to students and working professionals

OSHA Training
Occupational Safety and Health to deliver appropriate safety officer training to supervisors, employers & workers who face hazards on the workplace

ISO Lead Auditor
ISO Lead Auditor course is to provide adequate knowledge of Quality Management System to conduct and report a audit of an organization
For more Details contact:



it is supr in saftey life
Thanks for visiting us. we will update more and Kindly visithttp://greenwgroup.co.in/
good